Microsoft Entra Private Access is a Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) solution provided under the Microsoft Entra product family, designed to secure access to
private,
on-premises, &
hybrid applications.
It enables users to connect securely to private resources without relying on traditional VPNs, which can introduce latency, complexity, and security risks.
By implementing Microsoft Entra Private Access, organizations can move towards a Zero Trust architecture, ensuring that every user, device, and session is authenticated, authorized, and continuously verified.
Key Features of Microsoft Entra Private Access
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA):
- Replaces traditional VPN-based access with modern, secure connectivity.
- Access is granted based on user identity, device health, location, and other Conditional Access policies.
- Identity-Based Access:
- Enforces access control based on Azure AD user identities.
- Uses Conditional Access policies to assess real-time security signals like user risk, device compliance, and sign-in risk.
- Granular Application Access:
- Allows access to specific applications instead of entire networks, reducing lateral movement risks.
- Supports both on-premises and hybrid applications.
- Integration with Microsoft Security Stack:
- Works seamlessly with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to evaluate device compliance.
- Integrates with Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) for identity and access management.
- Seamless End-User Experience:
- Provides VPN-free access for private applications using the Global Secure Access Client.
- Offers fast, secure, and low-latency connections without the overhead of a traditional VPN.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Insights:
- Enables centralized monitoring of access patterns, user behavior, and compliance.
- Provides detailed analytics for security and troubleshooting.
How Microsoft Entra Private Access Works
- User Authentication:
- Users authenticate using Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD) and are evaluated against Conditional Access policies.
- Device Compliance Check:
- The solution checks if the user’s device complies with security policies, such as being managed by Intune or having updated antivirus software.
- Granular Access to Private Applications:
- Enforces access to specific apps or resources instead of exposing the entire network.
- For example, a contractor may only gain access to a specific app or server without accessing the corporate intranet.
- Traffic Routing Through Global Secure Access:
- Traffic is routed securely through Microsoft’s Global Secure Access infrastructure.
- This eliminates the need for direct network connectivity (e.g., via VPNs) to access private applications.
Use Cases
- Secure Remote Work:
- Employees and contractors can securely access private resources without relying on VPNs, ensuring a consistent and secure work-from-anywhere experience.
- Third-Party Vendor Access:
- Provide vendors or contractors with granular, limited access to specific apps while ensuring your network remains protected.
- Secure Hybrid Cloud:
- Enable secure access to both on-premises resources and cloud-hosted private apps in hybrid environments.
- Simplified IT Management:
- Centralize access controls and reduce the complexity of managing traditional VPN infrastructure.
Benefits of Microsoft Entra Private Access
- Enhanced Security:
- Uses identity-based authentication, real-time risk evaluation, and device compliance checks.
- Minimizes attack surfaces by replacing broad network access with app-specific access.
- Improved User Experience:
- Provides a seamless and faster experience compared to traditional VPNs.
- Reduces latency by routing traffic directly to applications.
- Simplified IT Operations:
- Eliminates the need for traditional VPNs and associated infrastructure.
- Centralized policy management through the Entra Admin Center.
- Cost-Effective:
- Reduces reliance on expensive VPN infrastructure while enhancing security.
Microsoft Entra Private Access vs Traditional VPN
| Aspect | Microsoft Entra Private Access | Traditional VPN |
|---|---|---|
| Access Type | Application-specific | Full network access |
| Security | Zero Trust-based | Perimeter-based |
| User Experience | Seamless, lightweight client | Often requires heavy VPN client |
| Latency | Low latency, direct app connection | Can introduce significant latency |
| Infrastructure | Cloud-native, simple to deploy | Requires on-premises VPN infrastructure |
| Granularity | Granular app-level access | Broad network-level access |
Licensing and Prerequisites
- Required Licenses:
- Microsoft Entra ID P1 or P2: For identity management and Conditional Access policies.
- Microsoft Entra Suite (includes Private Access): For private access functionality.
- Prerequisites:
- Users and devices must be registered in Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD).
- Global Secure Access Client installed on end-user devices.
- Private applications must be configured in the Entra Admin Center.
Next Steps
To start using Microsoft Entra Private Access:
- Review your organization’s private app access requirements.
- Configure Conditional Access policies in Microsoft Entra Admin Center.
- Deploy and test the Global Secure Access Client for seamless user connectivity.
If you’d like, I can guide you further on implementation steps, best practices, or any specific use case you’re interested in!
Lab:
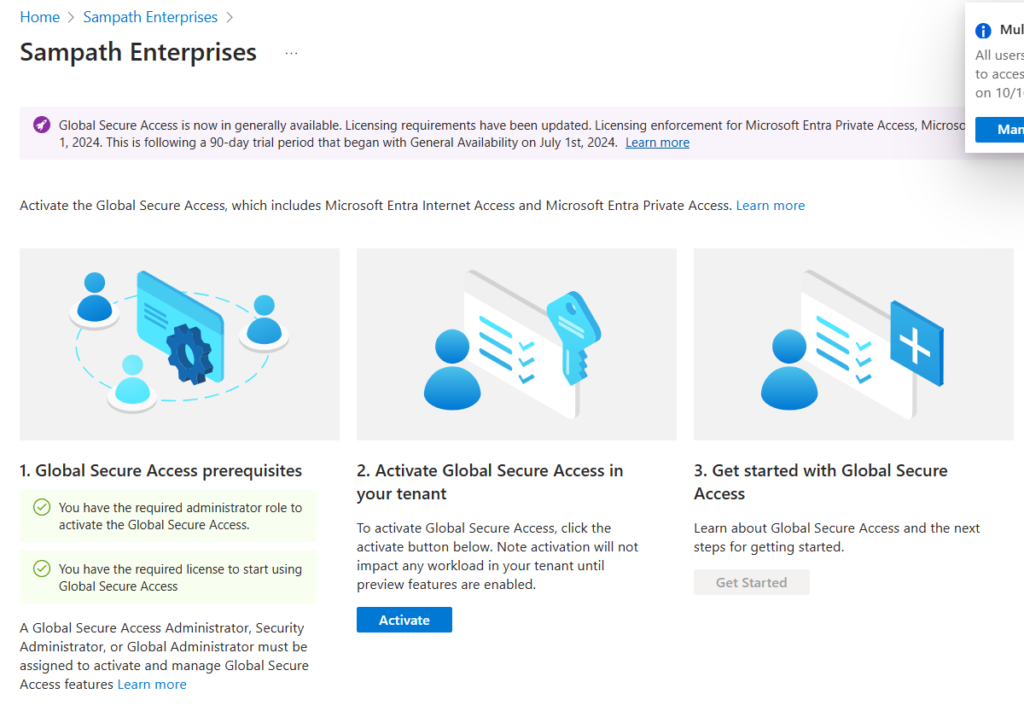





Reference : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=auGHYTXqSX4&t=13s


