Demoting a domain controller is a critical task that should be performed carefully to ensure that it does not negatively impact the Active Directory environment. Here’s a straightforward guide on how to demote a domain controller, which includes checking the FSMO roles and ensuring the replication is in a good state before proceeding with the demotion.
Step 1: Check the FSMO Roles
Before demoting a domain controller, it’s essential to know which server holds the Flexible Single Master Operations (FSMO) roles. You can do this by running the following command in Command Prompt as an administrator:
graphqlCopy codenetdom query fsmo
This command will list all the FSMO roles and the domain controller that holds each one. It’s crucial to ensure that the domain controller you plan to demote is not holding any FSMO roles. If it is, you’ll need to transfer these roles to another domain controller before proceeding.
Step 2: Check Replication Status
Next, verify the replication status to ensure that there are no replication issues before you demote the server. Run the following commands in Command Prompt:
bashCopy coderepadmin /replsummary
repadmin /showrepl
These commands help you confirm that all changes have been replicated to all domain controllers within the forest. Any replication errors should be resolved before proceeding with the demotion process.
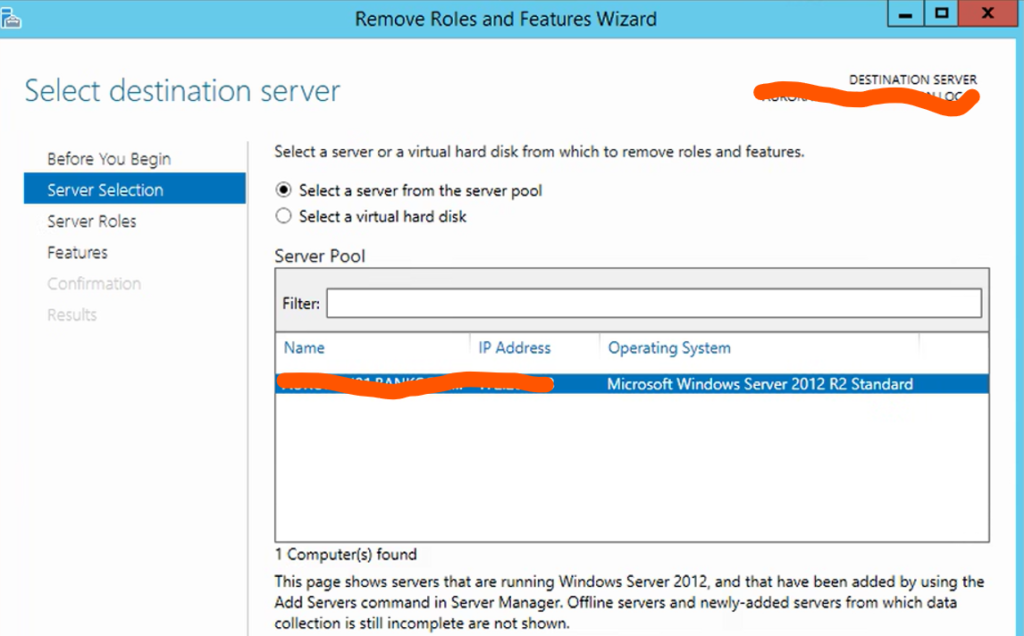
Step 3: Remove the Active Directory Role
Once you’ve confirmed that the FSMO roles are on a different server and that replication is functioning correctly, you can proceed to remove the Active Directory Domain Services role. This can be done through the Server Manager or using a PowerShell command, but here’s how to do it through the Server Manager:
- Open Server Manager.
- Click on Manage in the top right corner and select Remove Roles and Features.
- Follow the wizard until you reach the Roles page.
- Uncheck Active Directory Domain Services and any other associated roles that are no longer needed.
- Continue through the wizard and click Remove.
After restarted,
Remove the server from the Active Directory Sites and Services
Additional Considerations
The process of removing Active Directory Domain Services role can take about 30 minutes, depending on the system and network configuration. It’s important to plan for this downtime accordingly.
Conclusion
Demoting a domain controller should be done with careful planning and consideration of the roles it holds and its state within the replication topology. By following these steps, you can ensure a smooth transition and maintain the integrity of your Active Directory environment.
Remember to take necessary backups and have a recovery plan in place before making significant changes like this to your network infrastructure.


